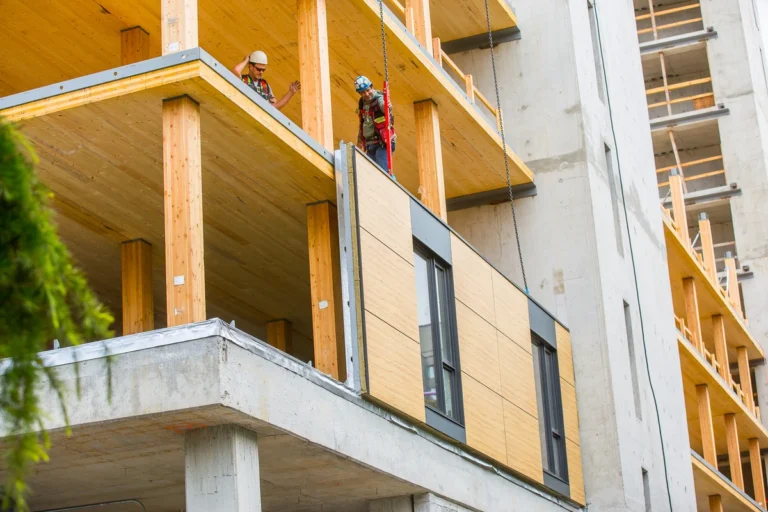
Introduction: Embracing the MMC Revolution
Modern Methods of Construction (MMC) represent a transformative leap in the way buildings are conceptualized, designed, and delivered. Unlike conventional bricks-and-mortar practices, MMC involves a variety of cutting-edge approaches such as off-site manufacturing, modular systems, and digital fabrication, all aimed at improving project efficiency, build quality, and sustainability.
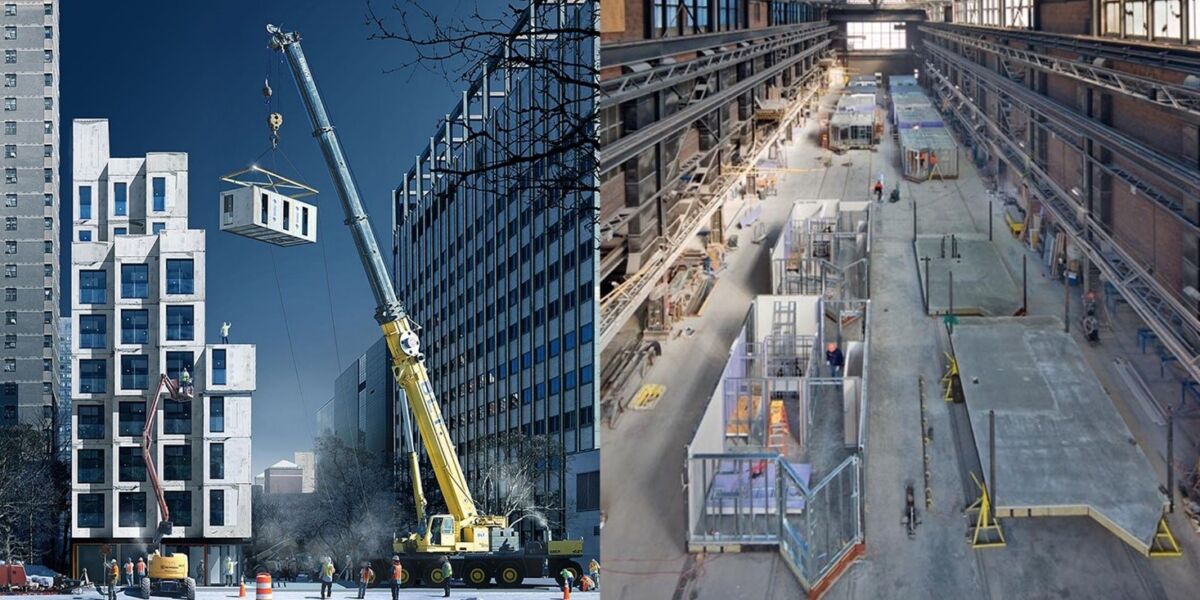

MMC first gained traction during the post-WWII era as a solution to housing shortages. Today, it provides scalable, high-performance construction solutions that address modern challenges including urbanisation, climate change, and labour shortages.
Defining MMC: Techniques & Technologies
Volumetric (Modular) Construction
It is possible to manufacture fully constructed 3D modules, such as entire rooms or floors, off-site and then transport them to the construction site for the purpose of facilitating speedy installation. The build time for these modules is reduced by 20–50%, which results in a significant improvement to the total project timeframes.
Hybrid & Pod Construction
Off-site manufacturing allows for the production of pre-finished parts such as kitchen pods, bathrooms, or balconies, which are then incorporated into bigger constructions. Consequently, this enables exact quality control while yet preserving flexibility in design integration.

On-site MMC Innovations
Technologies such as Insulated Concrete Formwork (ICF) and thin-joint masonry offer hybrid solutions even in situations where complete modular deployment is not practical. These technologies combine speed with greater thermal and acoustic performance resulting in hybrid solutions.

Digital & Robotic Fabrication
MMC combines Building Information Modelling (BIM) for improved planning, monitoring, and error reduction. This is accomplished via the use of technologies like as 3D printing, robotic arms, and virtual crane design.

Benefits That Define MMC
Speed & Cost Savings
- Faster Project Completion: Reduction in build time up to 50%.
- Lower Costs: Streamlined logistics and repeatable workflows can reduce costs by 10–20%.
- Optimised Supply Chain: Less material waste and fewer delays.
Quality & Consistency
- Controlled environments in factories enable:
- Higher dimensional accuracy
- Airtight building envelopes
- Fewer construction defects (down to 5% or less)
Sustainability Gains
- Up to 50% lower emissions compared to traditional builds
- Example: Ten Degrees Croydon achieved 42% carbon reduction
- Less material waste due to factory optimization
Safety & Site Experience
- Fewer workers on-site = reduced accidents
- Controlled indoor environments protect against weather risks
- Sites remain cleaner, quieter, and safer
Workforce & Productivity
- Less demand for traditional labour
- Supports digitally skilled jobs
- Encourages upskilling and long-term employment in controlled environments
Challenges & Strategic Considerations:
Capital Investment & Scale:
The initial investment required for manufacturing facilities and technology such as building information modelling (BIM) and robotic systems is substantial.
Transport Needs:
Road access, crane logistics, and site designs are all aspects that need to be meticulously addressed for volumetric modules.
Design Constraints:
In the absence of hybrid approaches, standardised modular design may restrict the creative potential of architectural designs (architecture).
Real-World Examples:
Goldsmith Street, Norwich
In order to achieve the requirements of the Passivhaus standard, this project, which was awarded the RIBA Stirling Prize, utilised timber panel MMC. It demonstrated that sustainable modular housing can be both elegant and efficient.

Ten Degrees, Croydon
This iconic skyscraper, which was built utilising volumetric modules and was constructed 42% faster than its predecessor, established new standards for speed and carbon economy in residential towers.
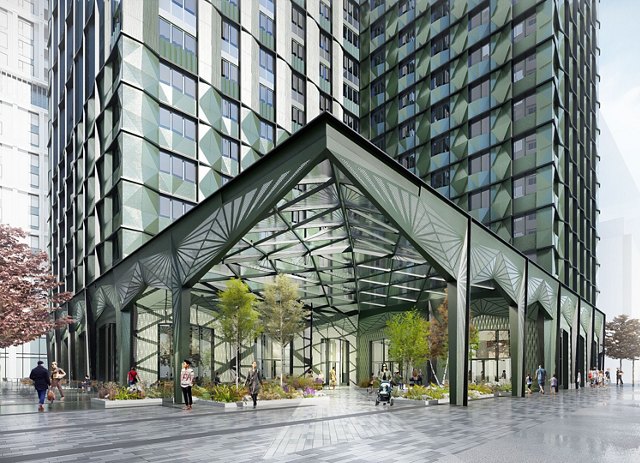

Modular Schools & Healthcare Infrastructure
MMC is an excellent choice for the speedy construction of medical units and educational facilities. The delivery of prefabricated units that are completely functional greatly reduces the amount of disturbance that is caused to communities.

The Road Ahead: Integration & Smart Construction:
Digital Ecosystem Integration
Through the use of real-time digital feedback loops, Building Information Modelling (BIM) connects the design, construction, and post-occupancy management processes throughout the building.
Robotic & Automated Fabrication
In the direction of completely automated construction processes, MMC is moving towards technologies such as virtual reality-assisted assembly and collaborating robots (co-bots).
Policy & Industry Alignment
The Construction Playbook, the MMC defining framework, and financing assistance through housing and infrastructure programs are all ways in which the government of the United Kingdom encourages the use of MMC strategies.
Conclusion: Unlocking MMC Potential
The construction industry is undergoing a change as a result of modern ways of building. They provide an unrivalled combination of speed, sustainability, safety, and cost-effectiveness, particularly when they are backed by policy and technology. Not only is MMC ready to alter buildings, but it is also positioned to reshape the fundamental foundations of how construction operations are carried out in the 21st century. Technology advancements in digital construction and factory-based assembly are continuing.
for more information visit this :
you can also visit:
https://www.architecturalrecord.com/articles/14229-continuing-education-modular-construction
https://edition.cnn.com/style/article/stirling-prize-2019-council-housing-winner-scli-intl