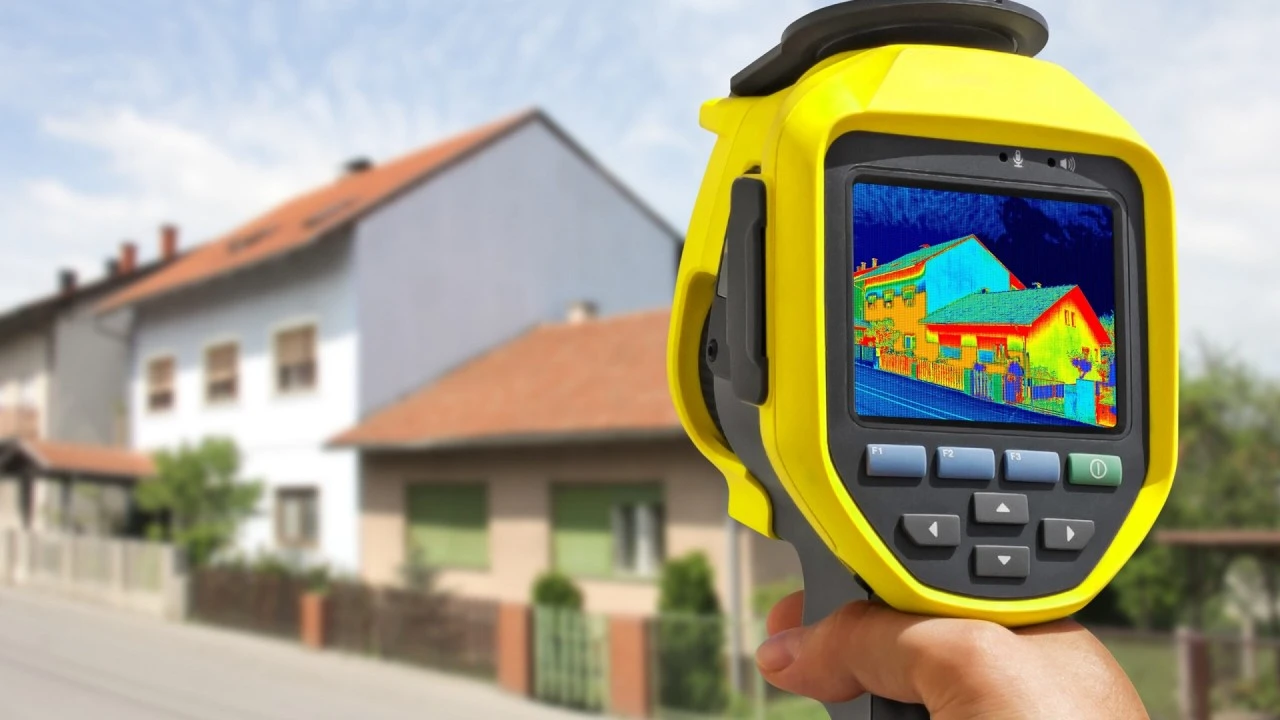
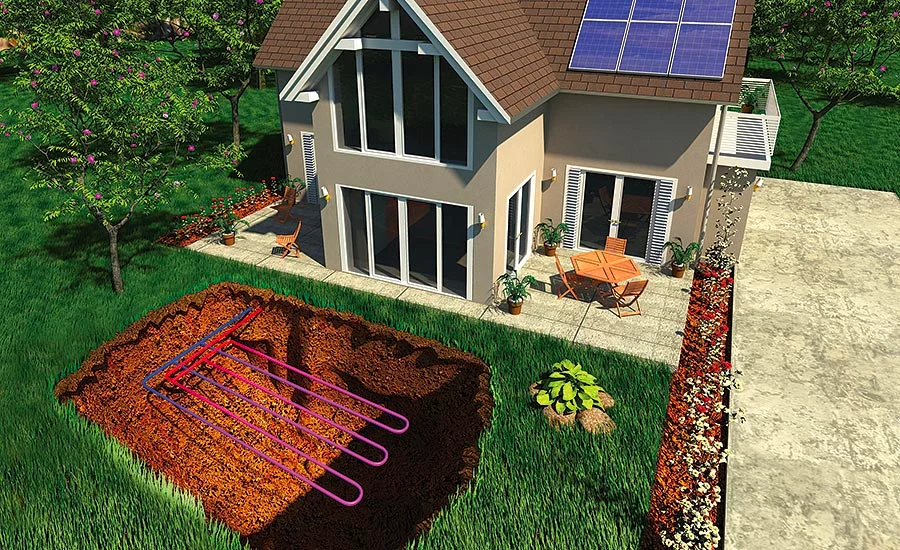
Everyone wants a beautiful home, but who doesn’t want a home that feels great all year long and saves their electricity expenditures by a lot? That’s the best dream of the modern world.
In the U.S., building or remodeling a house with an energy-efficient design isn’t a one-size-fits-all job. In Arizona, where it’s hot and dry, the tactics that work great will cause frostbite in Minnesota, where it’s quite cold. The only way to really be efficient and comfortable is to make your design fit your individual U.S. Climate Zone.
This Ultimate Guide goes over the most important rules to follow to make sure your home is a safe, comfortable place to live, no matter what the weather is like outside.

The Five Basic Principles of Efficiency
Before we get into the specifics of climate, any energy-efficient house design must follow these five basic rules. These are the most important parts of your building’s performance:
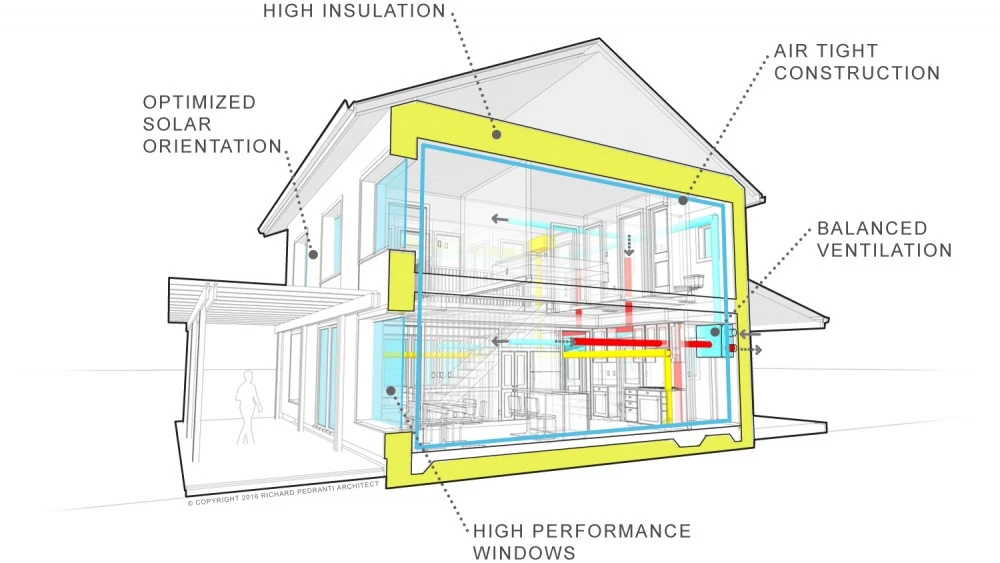
The Envelope That Is Super-Insulated and Airtight
The walls, roof, and floor of your home make up its “building envelope.” For the most comfort, this skin needs to be thick and completely sealed. A home with leaks can lose 25% to 40% of its conditioned air.
- Continuous Insulation (CI): Insulation must cover the entire structure without being broken up by wood studs or framework, which are “thermal bridges” that let heat in or out.
- Airtight Construction: To stop air leaks that aren’t regulated, you need to seal everything very well (with tape, caulk, and special membranes). This is the most cost-effective way to make energy use more efficient.
Doors And Windows That Work Well
Windows are usually the weakest part of the envelope. Windows are an investment in a design that is truly energy-efficient, not an afterthought.
- Low-E Glass: Coatings with low emissivity reflect heat, keeping summer heat out and winter heat in.
- Strategic Glazing: Depending on your individual U.S. Climate Zone needs, you can choose double- or triple-pane glass.
Getting Rid of Thermal Bridges
A thermal bridge is any element of the building’s outside that lets heat through more easily than the insulated parts, like a steel beam or wood stud that goes from the interior to the outside. Removing these things stops “cold corners” and lowers the risk of mildew and moisture, which immediately makes your home more comfortable.
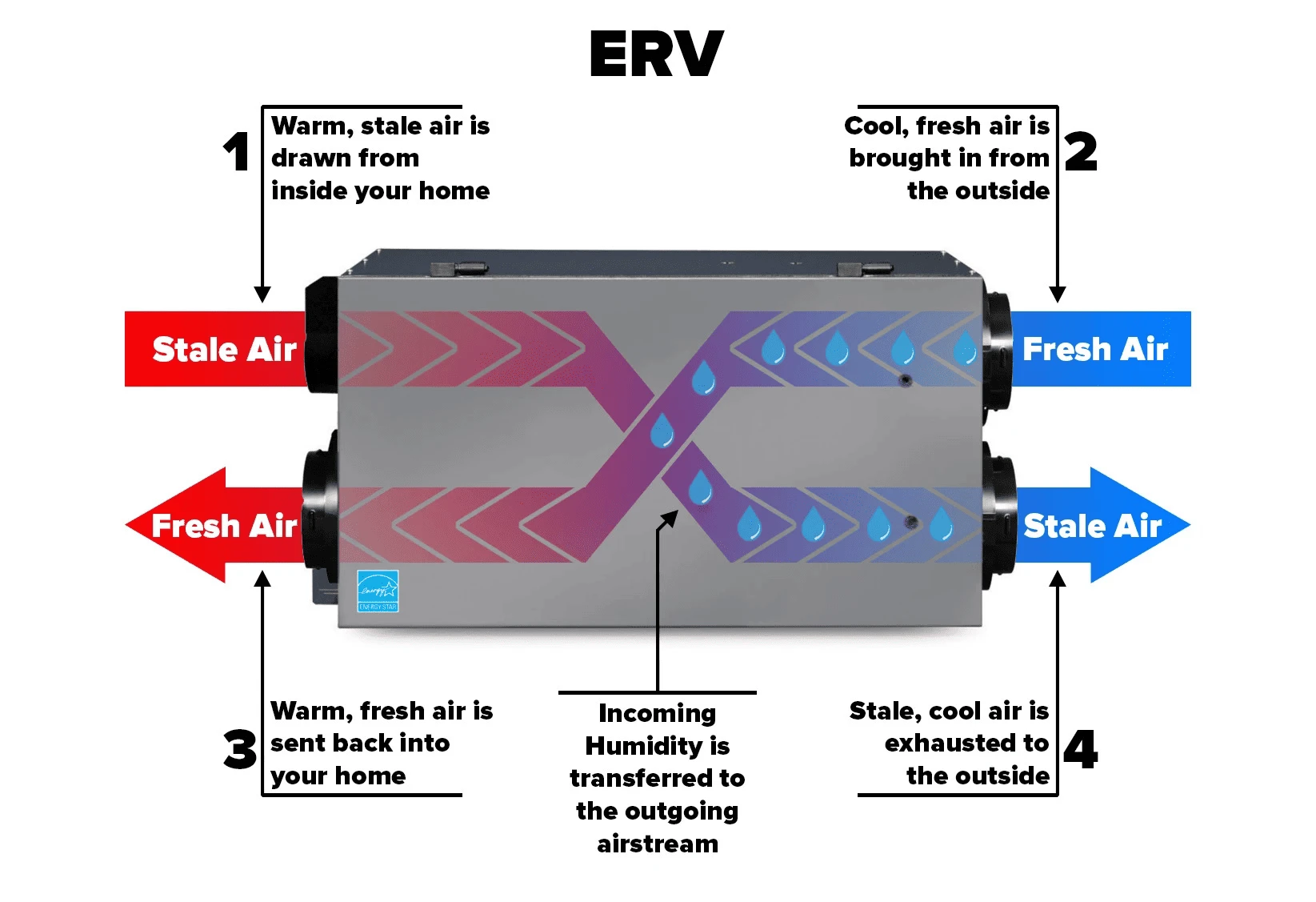
Balanced And Recovered Air Flow
You need a way to get fresh, nutritious air into your home if it is airtight. An Energy Recovery Ventilator (ERV) or Heat Recovery Ventilator (HRV) brings in fresh air from outside and takes the heat (or coolness) from the stale air that is going out. This doesn’t hurt your energy efficiency.
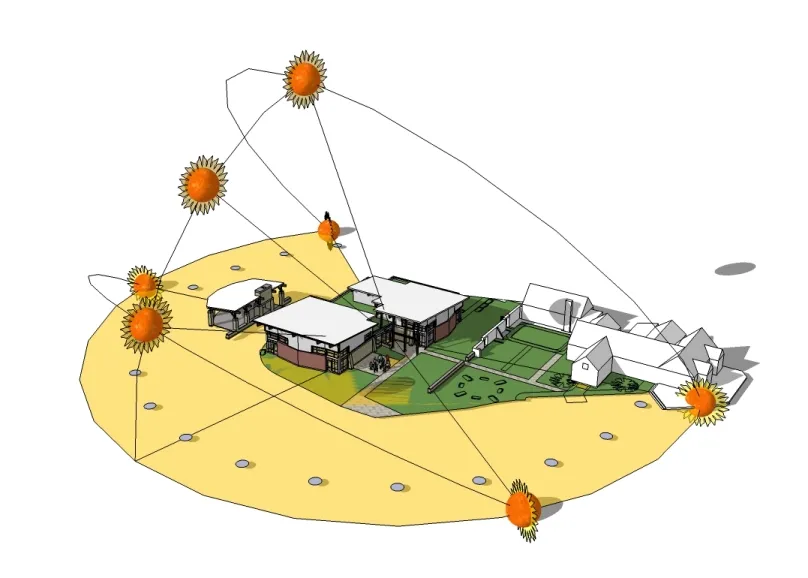
Orientation For the Climate (Passive Design)
This is when your location is most important. Passive Design is a way to use the sun and wind to your advantage. It can cut down on heating and cooling needs by 15–50%.
Designs for Different Climates: Strategies for Different Zones
The main way the U.S. Climate Zones are grouped is by how much heating and cooling they need. Depending on your zone, you will need to use different methods to apply the five basic principles:
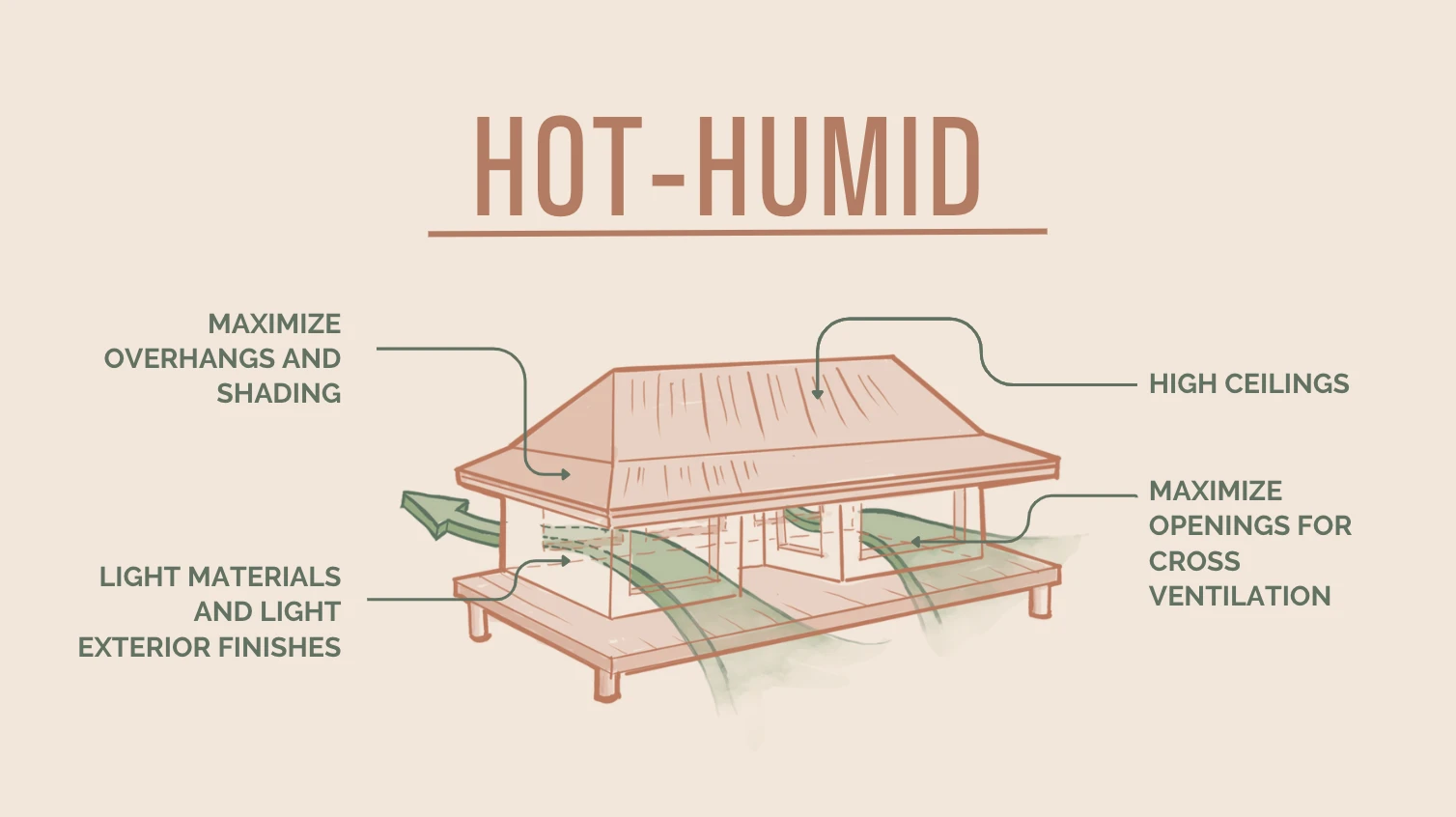
Zones 1–3: Hot and Hot-Humid Climates
- Goal: Keep moisture under control and keep solar heat gain to a minimum.
Important Design Tips:
- Roof: Put on a cool roof, which is made of materials that reflect a lot of light. Think about putting a radiant barrier in the attic.
- Orientation: Cut down on windows that face west and east, which get the most direct sunlight. Put most of the windows on the north and south sides, where they will be in the shade.
- Shading: Use deep roof overhangs, outside shutters, and trees that lose their leaves in the winter and get them back in the summer to shield windows.
- Mass: Don’t utilize a lot of heavy thermal mass indoors, like thick concrete flooring, because they can hold heat during the day.
Cold and Very Cold Climates (Zones 6–8)
- Goal: Get as much heat from the sun as possible and keep it from escaping.
Important Design Tips:
- Insulation (R-Value): To get the most insulation, walls should be R-30 to R-40 and roofs should be R-49 to R-60. Building walls with two studs is popular here.
- Orientation: Make the most of windows that face south so they can absorb passive solar energy during the day.
- Thermal Mass: Use stone fireplaces and concrete flooring indoors in locations that get solar gain to soak up heat and release it slowly throughout the night. This will keep inside temperatures stable for maximum comfort.
- Window Performance: Use triple-pane windows with low U-factors to keep heat from moving through them.
Zones 4 and 5: Mixed-Humid and Mixed-Dry Climates
- Goal: Find a balance between heating and cooling loads.
Important Design Tips:
- Compact Form: To keep heat in and out of the structure, make the design of the building simple and small, like a square. This will decrease the amount of space that is exposed to the outside.
- Mechanical Systems: These areas are perfect for high-efficiency heat pump technology that can both heat and cool, together with clever zoning to deal with temperature differences between levels.
- Daylighting: Use strategically placed skylights (with the right shade) and light shelves to introduce natural light deep into the building. This will cut down on the demand for artificial lighting without making it too hot.
Beyond the Walls: Systems for the Most Comfort
An efficient shell needs efficient mechanics to make living really comfortable.
Water, Heating, And Cooling
New house designs that save energy don’t need as many old-fashioned furnaces and air conditioners. Check out:
- Mini-Split Systems: These are ductless or ducted heat pumps that let you heat or cool only the rooms you are using at the time.
- Tankless water heaters heat water only when you need it, which saves energy that would otherwise be used to keep a big tank hot all the time.
Renewables on Site
Once you’ve cut down on your energy needs a lot with good design, using solar energy to satisfy the rest of your needs becomes quite cost-effective. A Passive House building needs so little energy that a modest solar array on the roof can turn it into a Net-Zero Home, which means it makes as much energy as it uses.
To design an energy-efficient house, you need to know a lot about your specific part of the American terrain. When you choose these energy-efficient house designs that are appropriate to your environment, you’re not just building a house; you’re making a safe haven that will be healthier, less expensive to run, and absolutely comfortable for decades to come.
For more blogs like this CLICK HERE!!
Reference: