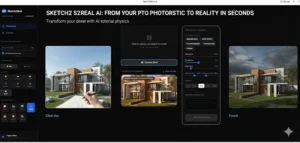
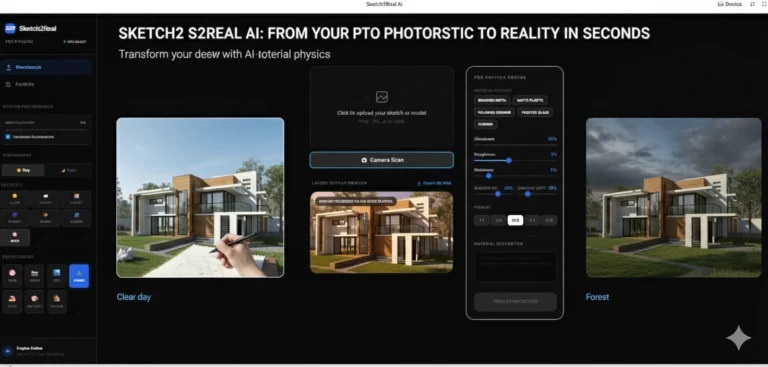
Introduction Redefining Architectural Vision
AR/VR, and digital twin technologies are not just futuristic novelties—they are practical, impactful tools revolutionizing modern architecture. As these innovations become more accessible, they’ll empower architects to design smarter, build better, and engage with people more meaningfully. Whether visualizing a tower in Denver or preserving a cathedral in Paris, the future of architecture is immersive, data-driven, and digital.
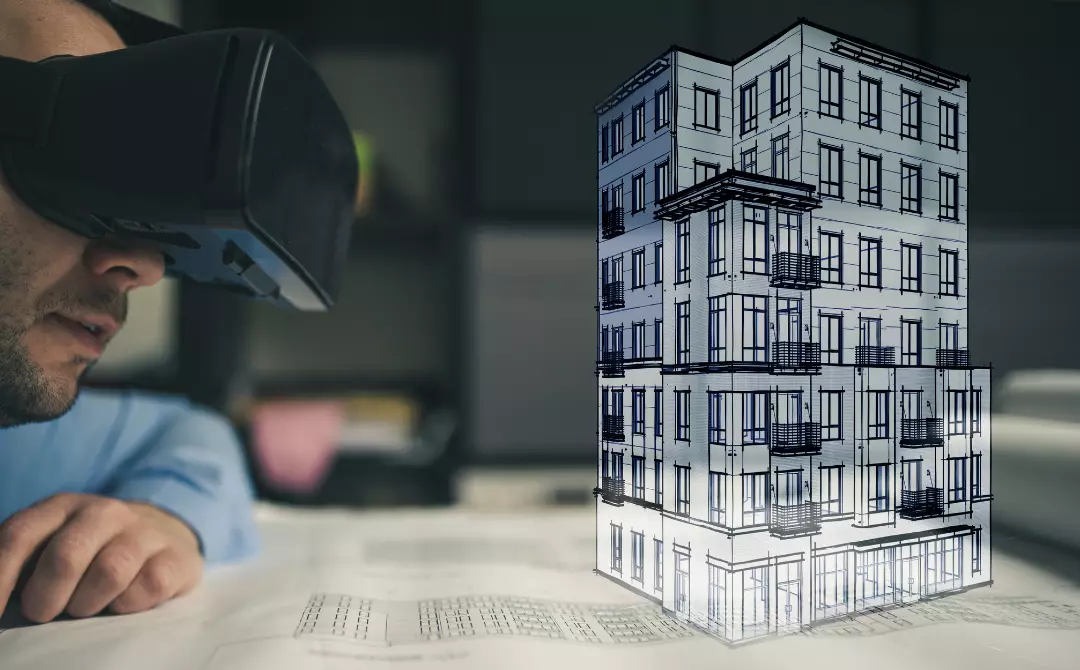

Understanding AR, VR, and Digital Twins in Architecture
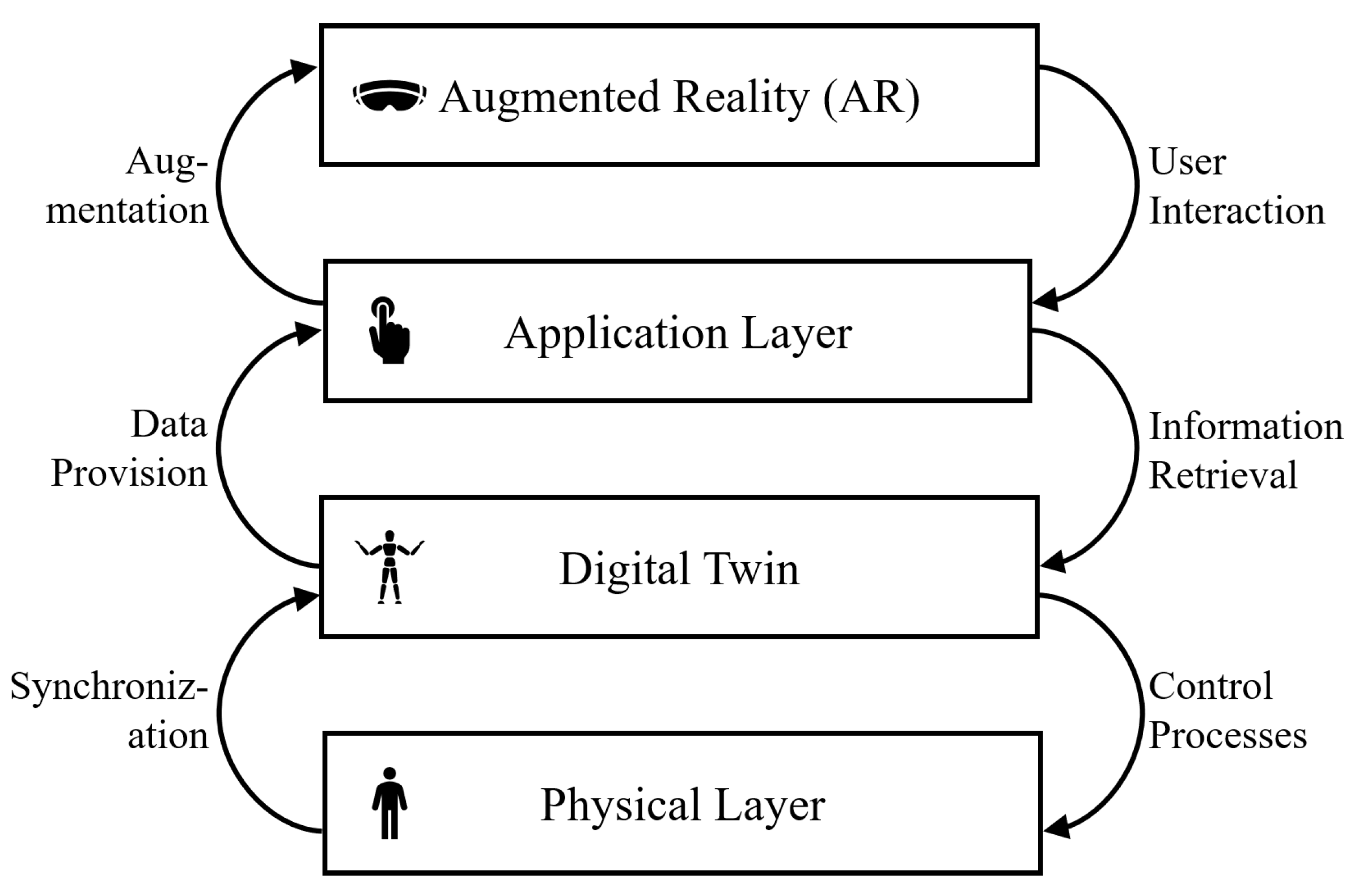
What is a Digital Twin?
A digital twin is a dynamic, real-time digital replica of a physical building or infrastructure. Powered by sensors, IoT devices, and BIM (Building Information Modeling), these virtual counterparts simulate environmental behavior—monitoring systems like HVAC, lighting, and structural integrity. Architects use digital twins to make informed decisions throughout a building’s life cycle, from design to operations.
Augmented Reality
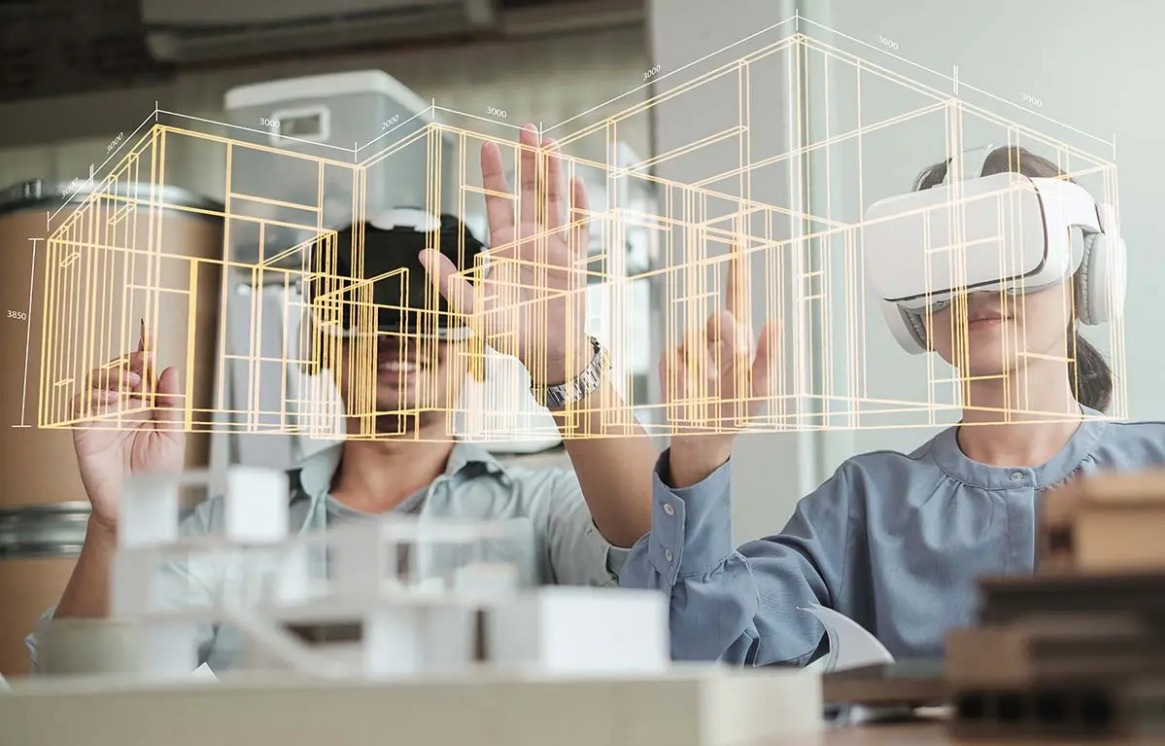
AR enables architects to project 3D models onto physical environments using smartphones or AR glasses. This helps clients and developers understand building scale and aesthetics before construction begins. For example, Valerio Dewalt Train used AR to visualize a Denver skyscraper—letting stakeholders walk around a life-sized model on-site.
Virtual Walkthroughs
VR creates immersive digital environments where users can virtually “walk through” unbuilt spaces. This 360° exploration improves decision-making by simulating real-world lighting, spatial layouts, and finishes. TEG Architects leveraged Samsung Gear VR to offer clients detailed views of proposed retail spaces, enhancing project alignment.
Key Applications of Modern Architecture
Design Review and Iteration
Combining AR/VR with digital twins allows design teams to simulate lighting conditions, occupant flow, and material performance—eliminating design flaws early and reducing rework.
Stakeholder Engagement and Public Input
In urban infrastructure, AR fosters transparency and community participation. Tampa Bay planners used AR-enhanced QR codes to showcase flood-resilience initiatives, gaining valuable public input.
Construction Inspection and Quality Assurance
Using AR on-site, construction managers overlay BIM models directly onto structures. This makes it easier to detect misalignments, ensuring greater accuracy and reducing costly corrections.
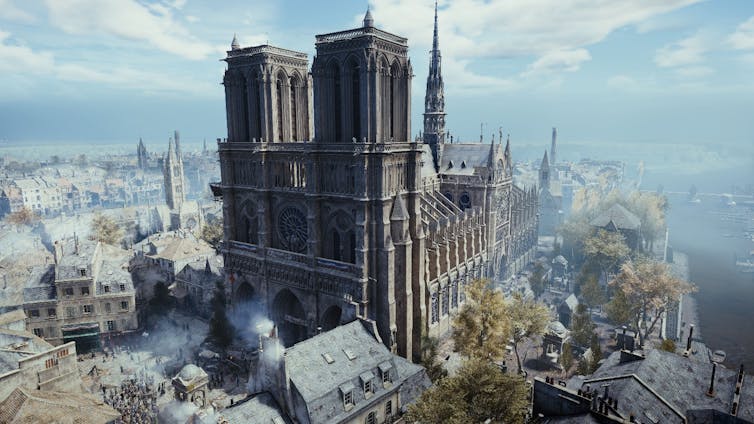
Restoration & Preservation
Historic structures like Notre Dame have been digitally reconstructed using VR and game engines like Unreal. These models serve both as educational tools and references for restoration.
Real-time Monitoring & Sustainability
Digital twins collect sensor data to track energy efficiency, thermal loads, and occupancy patterns—helping architects and engineers fine-tune buildings for optimal sustainability and cost savings.
The Technology Stack: Integration for Smart Design
To make AR/VR and digital twins work together, architecture firms rely on several core technologies:
IoT Sensors – Stream real-time data into twin models
BIM Platforms (Revit, ArchiCAD) – Hold structured architectural data
AR SDKs (ARKit, ARCore) – Enable model projection in real-world spaces
VR Engines (Unity, Unreal Engine) – Power immersive experiences
Cloud & AI Systems – Analyze building data for predictive maintenance and performance
Noteworthy Case Studies:
Virtual Singapore
This city-scale digital twin integrates urban planning, mobility data, and climate simulations, setting a benchmark for smart cities.

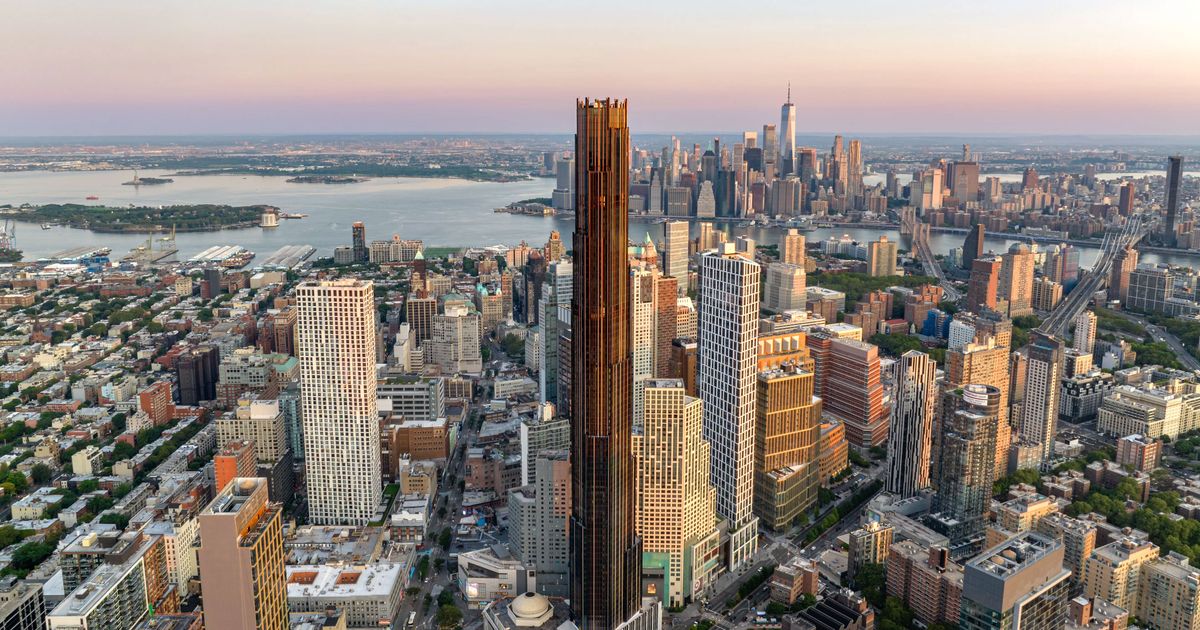
SHoP Architects, Brooklyn Tower
SHoP Architects employed Unity-powered digital twins to plan a 93-story skyscraper, optimizing its structural performance and energy use before breaking ground.

TEG Architects – Retail Innovation
VR walkthroughs helped retailers visualize layouts and lighting schemes before committing to construction, improving cost efficiency.

Denver Skyscraper AR Project
Developers used AR to visualize a high-rise structure at full scale—winning faster stakeholder buy-in through a captivating real-world demo.

Notre Dame – Digital Heritage
Epic Games’ photorealistic recreation of Notre Dame cathedral preserved priceless details, aiding restoration post-fire and making history accessible globally.

Tampa Bay Resilience Plan
nteractive AR models allowed residents to see how climate-resilient upgrades would impact their neighborhoods boosting civic engagement.

Benefits and Challenges:
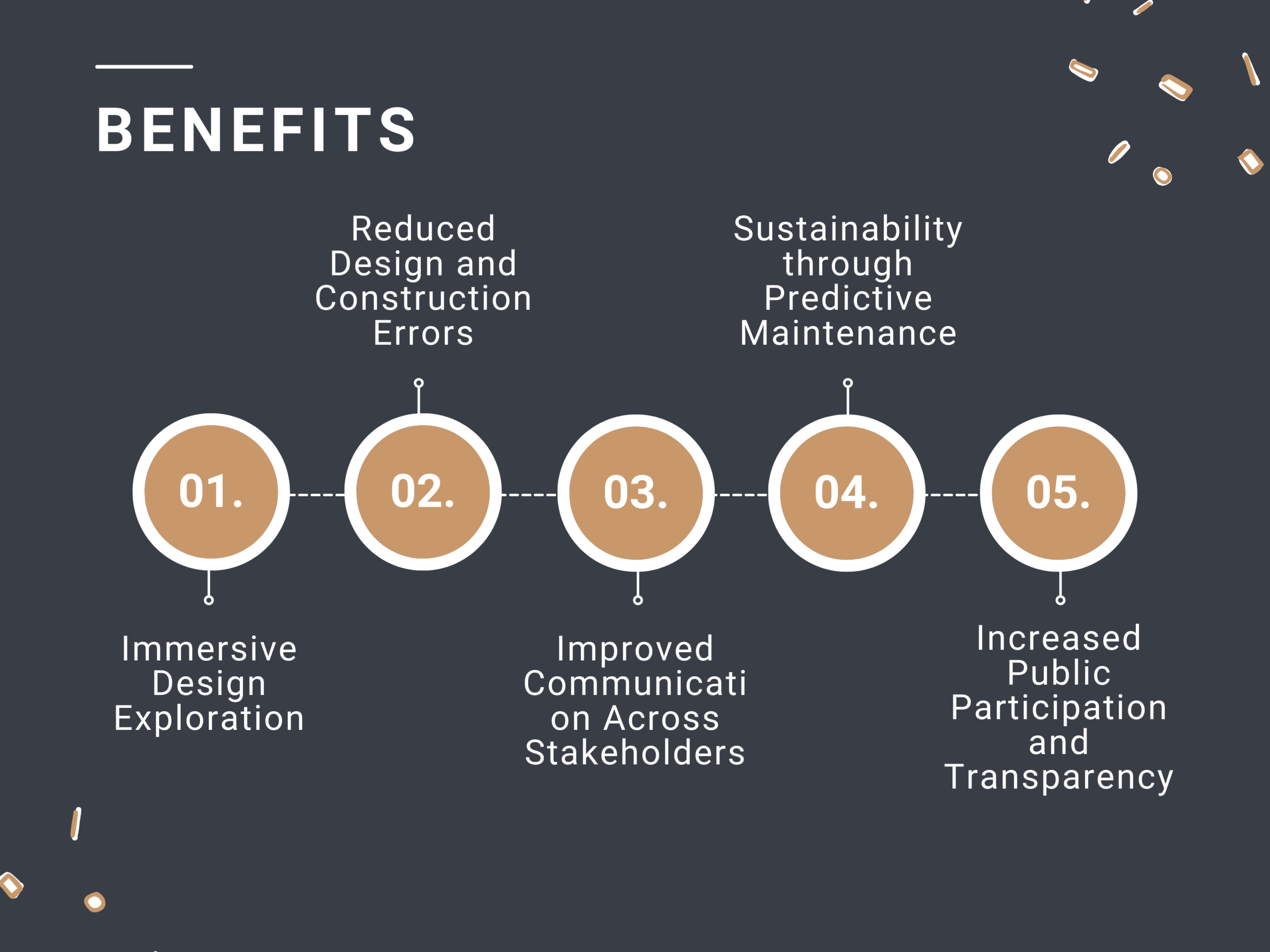
Benefits:
Immersive Design Exploration
Reduced Design and Construction Errors
Improved Communication Across Stakeholders
Sustainability through Predictive Maintenance
Increased Public Participation and Transparency
Challenges
- High Data Storage Needs
- Integration with Legacy Systems
- Cybersecurity for IoT Networks
- Upfront Costs & Training for Adoption
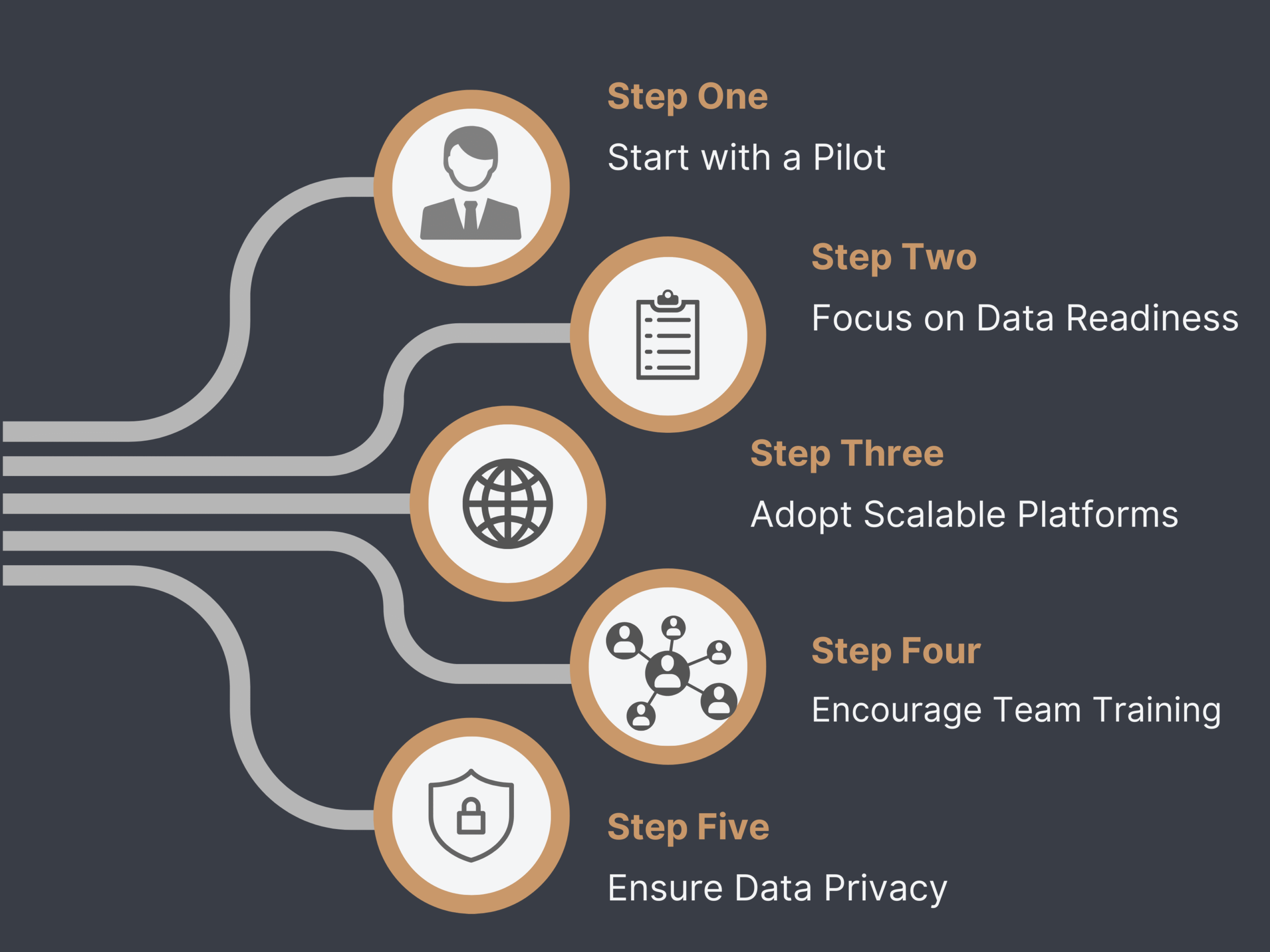
Best Practices in Adoption
- Start with a Pilot – Use AR on small design elements to build internal confidence.
- Focus on Data Readiness – Ensure BIM and IoT systems are compatible and up-to-date.
- Adopt Scalable Platforms – Choose tools that evolve with your needs and scale easily.
- Encourage Team Training – Invest in skill development for AR/VR tools across departments.
- Ensure Data Privacy – Encrypt digital twin data and secure cloud networks from breaches.
The Future of Architectural Immersion
AI-Driven Building Intelligence – Predict maintenance, airflow, and even user comfort.
City-Wide Digital Twins – From roads to skyscrapers, entire urban ecosystems will be simulated.
Virtual Collaboration Spaces – Architects, engineers, and clients will co-design in shared VR platforms.
Digital Heritage Libraries – Ancient buildings preserved forever through immersive experiences.
Conclusion
AR, VR, and digital twin technologies are not just futuristic novelties—they are practical, impactful tools revolutionizing modern architecture. As these innovations become more accessible, they’ll empower architects to design smarter, build better, and engage with people more meaningfully. Whether visualizing a tower in Denver or preserving a cathedral in Paris, the future of architecture is immersive, data-driven, and digital.


For more blogs like this you can visit :
you can also check this